Summary
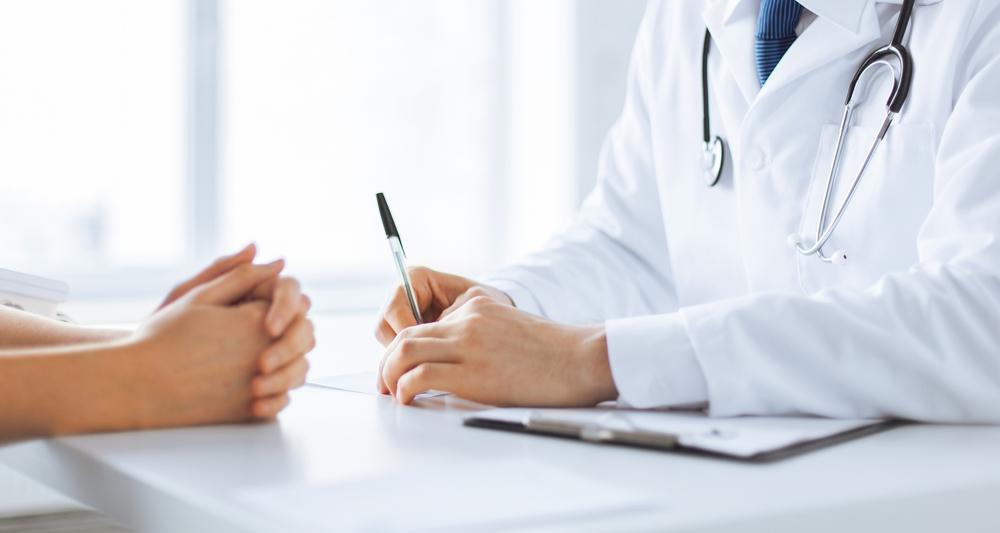
 Prostate biopsies are commonly done through the rectum due to the proximity of the prostate gland. The procedure involves taking samples from the prostate using a biopsy needle. The risk of cancer spreading to the rectum is not considered to be a significant concern, and the inflammation caused by the biopsy needs time to subside before further procedures like surgery or MRI can be done. Antibiotics are crucial to prevent infection after the biopsy.
Prostate biopsies are commonly done through the rectum due to the proximity of the prostate gland. The procedure involves taking samples from the prostate using a biopsy needle. The risk of cancer spreading to the rectum is not considered to be a significant concern, and the inflammation caused by the biopsy needs time to subside before further procedures like surgery or MRI can be done. Antibiotics are crucial to prevent infection after the biopsy.
Key Insights
Prostate biopsies are conducted through the rectum due to the proximity of the prostate gland to the rectal wall, facilitating easier access and sampling. The risk of cancer spreading to the rectum during a prostate biopsy is generally low, as the biopsy needle extracts prostate tissue directly into a collection device. Inflammation resulting from the biopsy can impact the accuracy of subsequent surgical procedures like robotic prostatectomy or MRI scans, necessitating a waiting period of six to eight weeks before these procedures. Antibiotics are crucial before and after a prostate biopsy to prevent complications such as urinary tract infections and sepsis. Overall, prostate biopsies via the rectum are considered safe and well-tolerated by most patients. However, potential damage to the rectum remains a concern during robotic prostatectomy due to the close proximity of prostate and rectal structures. For optimal imaging quality, MRI scans of the prostate should be postponed for six to eight weeks post-biopsy to allow inflammation to resolve.
Highlights
Prostate biopsies are typically performed through the rectum because of the close proximity of the prostate gland to this area. The risk of cancer spreading to the rectum during a prostate biopsy is minimal. Inflammation caused by the biopsy requires time to subside before proceeding with surgical procedures or MRI scans. Antibiotics administered before and after the biopsy are essential to prevent infection and other potential complications. These measures ensure that prostate biopsies are safe and effective procedures for diagnosing prostate conditions.