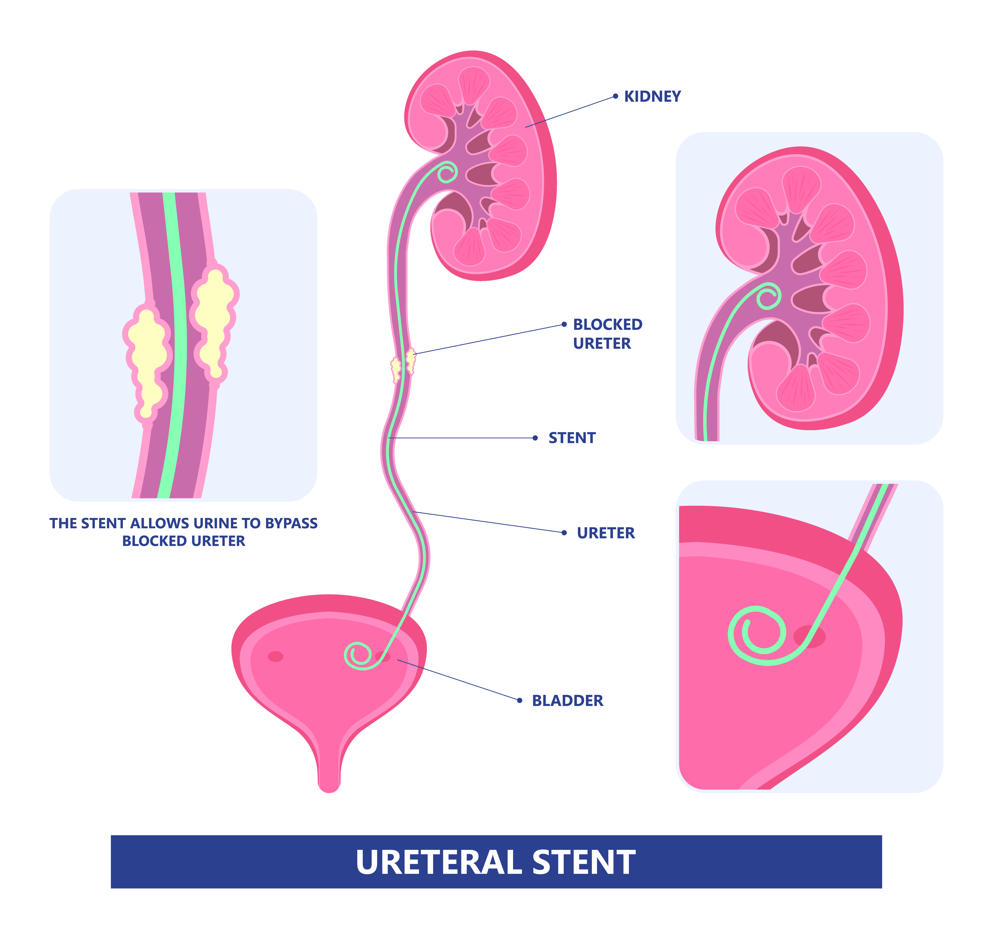
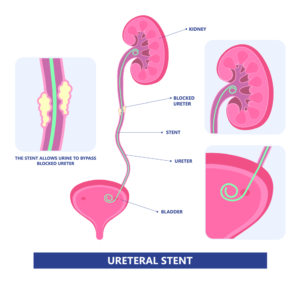
A ureteral stent is a small, flexible tube inserted into the ureter—the duct connecting the kidney to the bladder. It is used to ensure urine can flow from the kidney to the bladder, especially when the ureter is blocked or at risk of becoming blocked. Common reasons for ureteral stents include kidney stones, swelling from infection, or after certain surgical procedures.
Placement
The procedure to place a stent is usually performed under general or local anesthesia using a cystoscope, which is a thin tube equipped with a camera that is inserted through the urethra. The stent itself is designed with coils or anchors at both ends, ensuring it remains securely in place within the kidney and bladder.
Sensations and Side Effects
 While ureteral stents are effective, they may cause some discomfort or symptoms:
While ureteral stents are effective, they may cause some discomfort or symptoms:
- Urinary Frequency and Urgency: A constant feeling of needing to urinate, as the stent
- Pain or Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain in the lower abdomen, back, or during urination.
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which is common shortly after placement.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): A small risk exists due to the foreign body in the urinary system.
Activities and Lifestyle
- Regular activities can usually be resumed after a short recovery, but intense physical exertion should be avoided initially.
- Drink plenty of water to reduce discomfort and flush the urinary system.
Duration
Ureteral stents are generally temporary and are removed or replaced within a few weeks to months, depending on the underlying condition.
Removal
Stent removal is typically a quick and minimally painful procedure performed in a clinic using a cystoscope. If discomfort persists or symptoms worsen, such as fever, severe pain, or signs of infection, medical attention is needed.
Schedule a Ureteral Stent Consultation Today
A ureteral stent can provide relief from urinary blockages, ensuring proper kidney function and urine flow. If you are dealing with a condition that requires a stent, consulting with a skilled urologist is crucial for managing symptoms and ensuring a smooth recovery. Contact a local urologist today to schedule a consultation and discuss your treatment options.
Bibliography:
1. Smith, A. D., Badlani, G. H., & Preminger, G. M. (2007). Smith’s Textbook of Endourology. Wiley-Blackwell.
2. “Ureteral Stents: What to Expect,” Mayo Clinic, mayoclinic.org.
3. “Ureteral Stents in the Management of Ureteral Obstruction,” National Kidney Foundation, kidney.org.
4. Hyams, E. S., & Monga, M. (2008). “Ureteral Stent-Related Symptoms: Etiology and Management.” Indian Journal of Urology, 24(3), 339-343.
5. “Ureteral Stent Placement,” Johns Hopkins Medicine, hopkinsmedicine.org.